Introduction of Electric Fan Components
Electric fans play an essential role in keeping us cool and comfortable, making them a staple in homes, workplaces, and various settings worldwide. Yet, while we rely on their efficiency and ease, few understand what goes into an electric fan’s design and functionality. This article delves into the electric fan components, highlighting how each part contributes to performance, energy efficiency, and durability. From the motor to the control mechanisms, understanding these elements can deepen appreciation and help you make informed choices.
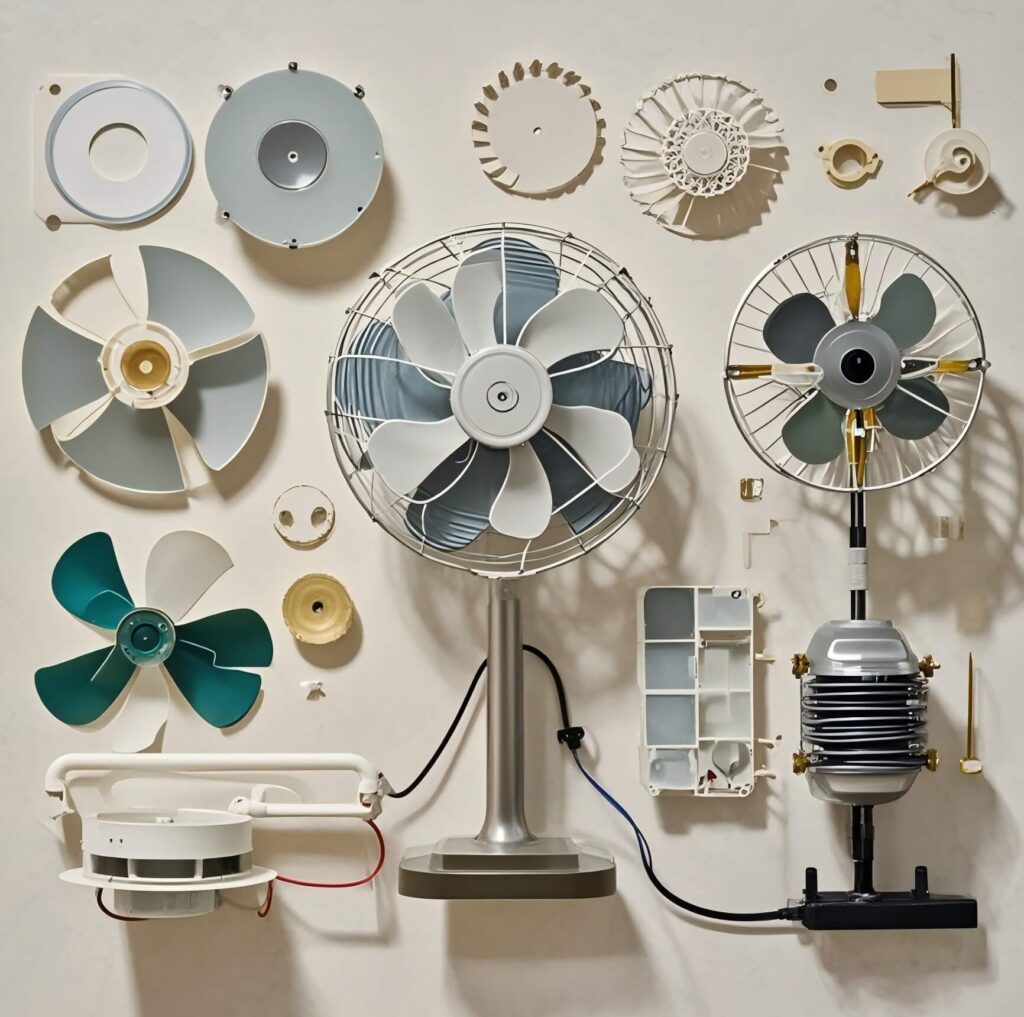
The Motor: The Heart of the Fan
A. Overview of the Motor’s Role in Generating Power
The motor is the powerhouse of any electric fan, converting electrical energy into the mechanical energy that drives the fan blades. By creating the necessary rotational force, the motor enables the fan to circulate air and maintain a consistent breeze.
B. Types of Motors Commonly Used in Electric Fans
There are several types of motors used in electric fans, with the most common being AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) motors. AC motors are traditionally found in most household fans due to their power efficiency and cost-effectiveness, while DC motors are popular in battery-operated and energy-saving models because they consume less power.
C. Importance of Motor Efficiency and Power Consumption
The motor’s efficiency directly impacts both the power consumption of the fan and its longevity. An efficient motor not only uses less energy but also reduces the wear on components, making it a more sustainable and economical choice over time.
The Blades: Creating the Breeze
A. Importance of Blade Design for Optimal Airflow
Fan blades are responsible for creating the airflow we feel, so their design significantly influences the fan’s cooling efficiency. Factors like blade length, width, and curvature contribute to the fan’s ability to push air effectively.
B. Materials Used for Fan Blades and Their Impact on Performance
Blades can be made from materials such as plastic, metal, or even wood in high-end designs. Plastic blades are lightweight and less expensive, but metal blades tend to be more durable and can generate more airflow. The material affects both the strength of the breeze and the fan’s noise level.
C. Blade Pitch and Its Effect on Air Movement
Blade pitch refers to the angle at which the fan blades cut through the air. A steeper pitch moves air more aggressively, providing a stronger breeze. However, higher-pitched blades may require more power to operate, impacting energy efficiency.
The Housing: Providing Structure and Safety
A. Overview of the Fan Housing’s Function
The housing is the protective case that surrounds the fan’s moving parts, serving as both a safety feature and a stabilizing structure. It prevents fingers and other objects from accidentally coming into contact with the blades, ensuring safer use.
B. Common Materials Used for Fan Housing and Their Advantages
Fan housing is often made from plastic or metal. Plastic is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective, while metal provides more durability and is typically found in commercial or heavy-duty fans. The material affects the fan’s lifespan and robustness.
C. Noise Reduction Features in Modern Fan Housings
Many modern fans are equipped with noise reduction features within their housing design. Innovations such as rubber mounts and improved airflow channels help to minimize operational noise, enhancing comfort and usability, especially in quiet settings like bedrooms or offices.
The Control Mechanism: Adjusting Speed and Settings
A. Role of the Control Mechanism in Regulating Fan Speed
The control mechanism is the part that allows users to adjust fan speed and sometimes even its direction. By adjusting the settings, you can control the airflow strength and circulation to suit different preferences or needs.
B. Types of Fan Controls: From Basic Switches to Remote Controls
Electric fans offer a variety of control options, from basic on/off switches to advanced digital or remote controls. Some fans include touch-sensitive panels, smart connectivity options, or wall-mounted controls, giving users greater flexibility and convenience.
C. Additional Features: Programmable Timers and Oscillation
Many fans now feature programmable timers, allowing users to set specific operating times, and oscillation settings to increase the reach of airflow in a room. These features add to the functionality and customization of the fan.
The Power Source: Energizing the Fan
A. Different Types of Power Sources for Electric Fans
Electric fans primarily run on either AC or DC power sources. AC-powered fans are more common in household and office settings, while DC-powered models, including rechargeable and battery-operated fans, offer portability and can be used in places without direct power access.
B. Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency
AC fans tend to consume more power, but modern energy-efficient models have been designed to reduce consumption. DC fans are typically more energy-efficient, making them a popular choice for those looking to save on electricity or reduce environmental impact.
C. Battery-Operated Fans and Their Benefits
Battery-operated fans are ideal for outdoor use, camping, or during power outages. They offer the convenience of portability and energy independence, which makes them a practical choice in various scenarios.
Conclusion of Electric Fan Components
Electric fans may appear simple, but they are built with several intricate components working in harmony to provide effective and reliable cooling. From the motor that powers the device to the blades that generate airflow, and from the control mechanisms to the housing that ensures safety, each part has a critical role in the fan’s operation. A well-rounded understanding of these elements not only aids in choosing the right fan but also enhances its maintenance and longevity. As technology continues to evolve, we can look forward to more energy-efficient, quieter, and smarter fans, making them an even more indispensable part of our lives.
FAQ of Electric Fan Components
1. How can I improve the airflow of my electric fan?
To enhance airflow, ensure the fan is positioned in an open area without obstructions. Regularly cleaning the blades and housing can also improve air circulation.
2. Are there any safety tips to keep in mind while using an electric fan?
Yes, avoid placing the fan in damp or wet areas, keep fingers and objects away from the blades, and regularly check the power cord for wear or damage to prevent electrical hazards.
3. What should I do if my electric fan stops working?
If your fan stops working, check for any loose connections, clean the motor and blades, and consult the user manual. For serious issues, consider seeking professional repair services.
4. Is it better to use an AC-powered or battery-powered fan?
This depends on your needs. AC fans are reliable for continuous use in homes, while battery-powered fans are ideal for portability and use in areas without power outlets.
5. How do I clean and maintain my electric fan for optimal performance?
Regularly unplug the fan and clean the blades, housing, and motor area. Avoid using water on the motor, and ensure the fan is completely dry before reconnecting it to power.
